Elaphe guttata guttata
Type: reptile
Status: endangered
Species Guide
Corn snake
Elaphe guttata guttata
Species Type: reptile
Conservation Status: endangered
Identification
The corn snake (sometimes known as the red rat snake) is a beautiful and docile species. This is a long snake, with a flat belly and flat sides (like a loaf of bread). Ground color is variable, and can be orange, brown or gray. Orange, red or brown blotches outlined in black run down the middle of the back, with smaller blotches on the sides. Some individuals may have stripes rather than blotches. The head is marked with a blotch shaped like a spear point, which splits towards the neck. The underside is white, marked with large black squares on the belly and stripes on the underside of the tail. Scales are smooth on most of the body and weakly keeled on a few middorsal rows; anal plate is divided. Adults are usually 2.5 to 4 feet in length, but can grow as long as 6 feet.
The corn snake molts several times a year, shedding its outer layer of skin to accommodate the growing animal. Prior to shedding, the snake appears duller in color and the eyes become cloudy. During this vulnerable time, the corn snake seeks and rubs against bark, logs, or rocks to remove the old skin. Once a tear is made, the snake crawls out of the old skin, leaving its shed behind. After shedding, the snake appears more vibrantly colored and resumes normal behavior. The complete process of shedding, from
clouding to sloughing off the old skin, spans about a week or longer.
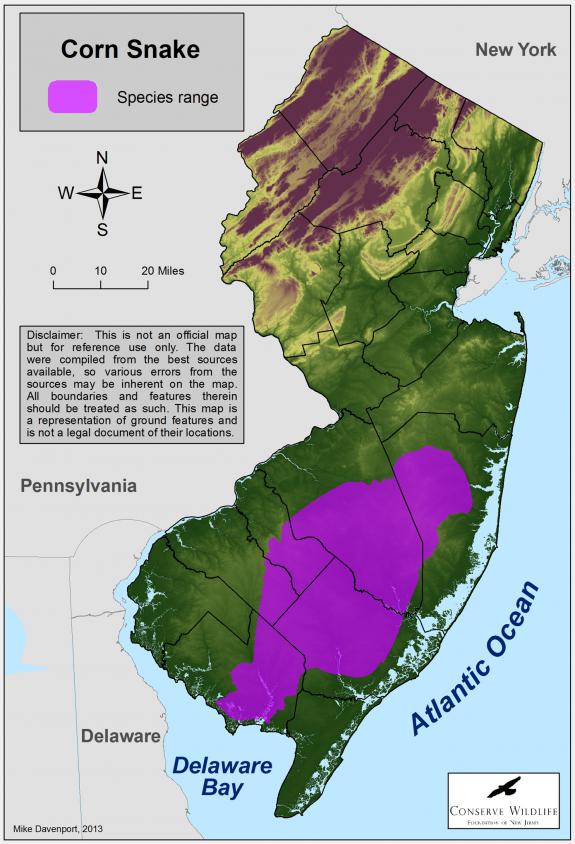
Distribution & Habitat
Native to the Pine Barrens of southern New Jersey, the corn snake historically inhabited sites throughout Ocean, Burlington, Cumberland, and Atlantic. Although still present throughout these regions, this reptile has been lost from many sites because of habitat destruction.
Corn snakes prefer mature, upland pine-oak forests with an understory of low brush that contain uprooted trees, stump holes, and rotten logs. Soil types typically include sands and loams. Corn snakes inhabit locations containing a water source, such as a stream or pond. Open field and forest edges are used for foraging. As a highly fossorial species, they seek cover in hollow logs, railroad ties, and the foundations of old buildings as well as under boards and logs. Abandoned buildings or foundations may be used for nesting or hibernating.
Diet
The corn snake’s diet is dominated by small mammals but also includes birds, reptiles, and insects. In the New Jersey Pine Barrens, white footed mice and fence lizards make up the majority of the corn snakes’ diet. Adult snakes also prey upon small birds, eggs, chicks, moles, mice, chipmunks, and voles. Hatchling snakes feed primarily on fence lizards and insects.
The corn snake is a constrictor meaning that the snake suffocates its quarry by tightly wrapping its body around the prey. Corn snakes stealthily stalk their prey until they are within striking range. With one lightning-speed motion, the snake lunges at its target, grabbing the animal with its mouth and constricting its body around the prey. Once the prey is dead, the snake begins to consume it, swallowing it whole, headfirst. Snakes are able to consume sizeable prey by unhinging their jaw bones while swallowing and stretching their skin to accommodate their prey. The corn snake requires at least several days for digestion.
Life Cycle
Corn snakes are active May through September and are mostly nocturnal; especially during the hot summer months. Warming temperatures in late April and early May arouse corn snakes from hibernation. From May to early June, the snakes mate. The exact date of egg laying, which ranges from mid- to late July, varies with environmental conditions, the physical state of the female, and the date of mating. Clutch size ranges from 5 to 14 eggs, depending on prey availability and the health of the female. The female, which may deposit her eggs at the same location each year, nests in old railroad ties, hollow logs or stump holes. The heat generated from the rotting of wood or logs may facilitate incubation. The eggs, which incubate for five to seven weeks, hatch in September. Hatchling corn snakes measure approximately 11 inches in length.
In October and November, cooling lead corn snakes to retreat to their wintering sites. Underground burrows, stump holes, or hollow railroad ties located beneath the frost line serve as hibernacula. It is common for corn snakes to use the same hibernaculum in consecutive years.
Current Threats, Status, and Conservation
The greatest threats to corn snakes are severe habitat loss and illegal collecting for the pet trade. Their specialized habitat requirements make them especially vulnerable to habitat loss and fragmentation. As habitats are fragmented, corn snakes become more vulnerable to genetic isolation, road mortality, human persecution, and illegal collecting. Off-road vehicle use may result in road mortality of basking or traveling snakes.
Illegal collecting of corn snakes is a persistent problem. Because of its beauty and ease of care in captivity, the corn snake is highly prized by collectors. Poachers often destroy nesting sites and hibernacula to remove adult snakes, eggs, and young. Many historic corn snake populations have been lost due to habitat destruction and poaching.
The protection of upland forest habitats is critical to the conservation of corn snakes in New Jersey. Parcels that contain corn snakes or suitable habitat should be protected from habitat destruction. Off-road vehicle use should be seasonally prohibited near known corn snake sites.
Forest management and man-made hibernacula can be used to improve habitat for corn snakes. Corn snakes prefer forests that rely on fire to suppress the growth of oaks. Controlled burns or selective cutting can be used to maintain a pine-dominated habitat. If selective cutting is implemented, the resulting logs and branches can be used to create denning mounds for snakes or brush piles for their prey. Because corn snakes accept man-made hibernacula, they can be created within areas of suitable habitat.
New hibernacula, as well as established sites, should be monitored regularly by conservation officers. If poaching is suspected, strong efforts must be made to apprehend and prosecute illegal.
References
Text derived from the book, Endangered and Threatened Wildlife of New Jersey. 2003. Originally written by Sherry Liguori.
Scientific Classification
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Reptilia
- Order: Squamata
- Family: Colubridae
- Genus: Elaphe
- Species: E. guttata