New Jersey’s Key Role in the Monarch Migration
The Garden State annually hosts swarms of southbound Monarch Butterflies
By: Kendall Miller, Project Coordinator
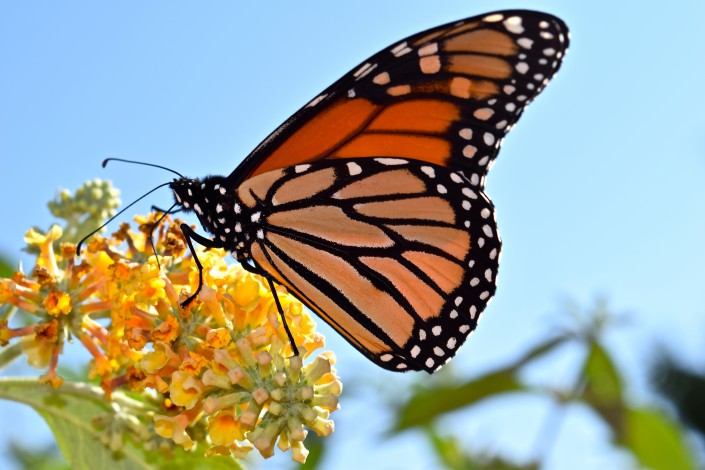

Monarch has been a conservation buzz-word for the past decade when data revealed that the population had appeared to be on the decline. Then in 2013, the population of wintering monarch butterflies in Mexico reached an all-time low that jolted scientists, environmentalists, and enthusiasts across the nation.
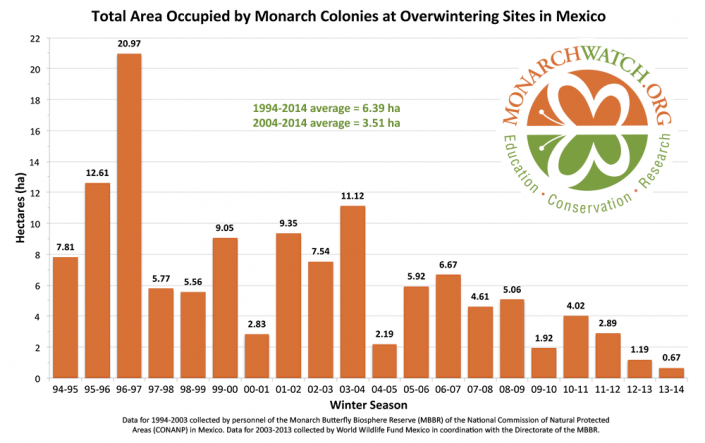
This marvelous and iconic lepidopteran is found throughout the continental United States. Its 3,000 mile long migration is an amazing natural phenomenon. The news of population declines in Mexican wintering sites inflamed concern and incited action. Many groups have since created partnerships, implemented programs, and conducted research to understand more about this widely known yet still mysterious insect.
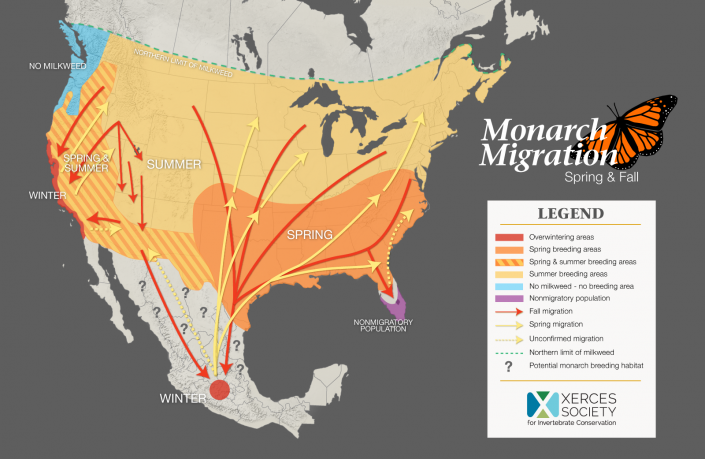
The location of wintering monarchs was a complete mystery until 1975 when the remote wintering sites were discovered in transvolcanic mountain ranges in Mexico. Much is still to be discovered about the migration pathways even within the United States, and doing so will answer questions which will inform conservation and management of this species which faces multiple threats during every aspect of its expansive journey.
Glider pilots have observed monarch butterflies at an altitude of 1200 meters (Gibo 1981). Migratory flights at these altitudes can allow insects to disperse against wind directions found at lower altitudes.
But first, a little bit about biology and the annual life cycle
The monarch’s annual lifecycle is a really marvelous and multifaceted journey – it can be thought of as a multigenerational relay race.
Monarch butterflies, just like other lepidopterans, metamorphosis from caterpillar to butterfly. The big thing that sets them apart is the migration they make annually. (Although there are many other species of moths and butterflies, and other insects as well that migrate – the monarch is arguably the most well recognized example http://texasento.net/migration.htm).
Temporal cues and an innate determination drive these ambitions fliers to travel as far north as the Canadian border. In the search for milkweed and favorable temperatures – possibly to avoid disease pressures – monarchs fly north to reproduce and recolonize across North America each year.
They leave overwintering grounds in Mexico in early spring. Along their route the monarchs will mate and reproduce. Their lives are lived within a short couple weeks, and their offspring will continue the migration northwards in search of food and milkweed.
When the seasons shift in late summer and early fall, the last generation of monarchs will begin a southbound journey, instinctively traveling to wintering sites in Mexico (there are a few populations that overwinter in California and Florida – but the large majority are thought to return to Mexico). This generation will be responsible for making the longest trek of the migration to wintering grounds. These monarchs enter reproductive diapause – the state where the body will temporarily pause reproduction – until the following spring. These monarchs will spend the winter roosting in trees in Mexico until spring when they will take up the first leg of the relay north.
This last generation from the previous year now makes up the first generation of the present year – and will pass the baton on to their offspring as the cycle starts anew.
The role of the Garden State
So what part does New Jersey play in the grand scheme of this massive population?
The Atlantic coast migration was once characterized as “aberrant”, a fluke of sorts – the result of southbound monarchs being blown off course. Research and monitoring conducted in Cape May and published by Walton and Brower (1996) in The Journal of the Lepidopterist’s Society have supported the hypothesis that a migration along the Atlantic coast is part of the monarch’s normal fall migration.
What does a monarch have in common with a hawk?
Walton and Brower (1996) have proposed the idea that monarch butterflies could display similar flight patterns to that of migrating hawks. Utilizing an elliptical flight path during the fall south-bound migration, the model suggests that these birds take advantage of prevailing winds by first traveling east and then west, thus providing a quicker and more energetically-efficient route. Could monarch do the same?
New Jersey – Southern New Jersey and Cape May in particular – is historically recognized as a concentration area for southbound monarchs during the fall migration to wintering grounds. Hamilton (1885) [expressed his wonder of the] characterized the September 1885 monarch migration at Brigantine, New Jersey as “almost past belief … millions is but feebly expressive … miles of them is no exaggeration.” Reports of trees “more orange than green” is no exaggeration, as monarchs congregate en masse in prime roosting spots to warm and rest.
But why is this important? The monarchs migrating through Cape May seem to be representative of the entire North Eastern population – and therefore it offers the opportunity to collect quantitative data on populations in addition to other annual counts. The fourth of July counts focus on quantitatively monitoring the Northeastern population of monarchs as they arrive in the spring and summer. Therefore this data can be used to analyze population trends.
What part can New Jersey residents play?
Monarchs are traveling across New Jersey May through October. There are plenty of simple ways you can help protect this iconic species.
- Plant native species of flowering plants – monarchs and other insects (like bees) rely on a healthy diversity of nectar sources. Planting a wildflower garden is a quaint, ecological-friendly way to create habitat, and not to mention, make less work watering and money spent purchasing plants. Check out the Native Plant Society or Jersey Friendly Yards to get started. http://npsnj.org/ http://www.jerseyyards.org/
- Share this article, talk about environmental issues, and get informed. Show your support and share your concern for the wellbeing of this (and other) species!
- Rear monarchs. At home or in classrooms, rearing wild monarchs and releasing them is a rewarding and educational way to contribute.
- Participate in tagging and monitoring projects. Monitoring and tagging projects take place in the summer and fall for New Jersey Monarchs. You can also contribute simply by reporting your sightings on these websites.
- Report sightings and tag monarchs with Monarch Watch.
- Be a Citizen Scientist by participating in the Journey North mapping and monitoring project by reporting sightings.
- In Cape May, the Cape May Monarch Monitoring Project conducts fall migration censuses each year.
- The North American Butterfly Association is responsible for the Fourth of July butterfly count census.
LEARN MORE






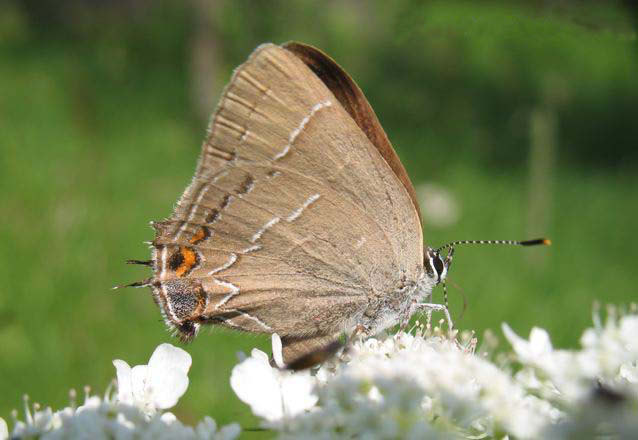
 Hickory hairstreaks can be seen from mid-June to early August in the northern half of the state. Their habitat consists of deciduous and second growth forests and adjacent fields. The forests in its habitat almost always consist of hickory trees, as they are the primary food plant of its caterpillars. Adult butterflies feed on the nectar of a variety of flowering plants including common milkweed, New Jersey tea, and white sweet clover. The hickory hairstreak is a relatively small butterfly with a wingspan of approximately 1 to 1 ½ inches. It is rarely seen with its wings open and is identified by the dark postmedian “dashes” and white outline on the underside of its grayish brown wings. On the hindwing, there is a pale blue patch that extends inward further than the adjacent orange and black spots. There is one tail on each hindwing.
Hickory hairstreaks can be seen from mid-June to early August in the northern half of the state. Their habitat consists of deciduous and second growth forests and adjacent fields. The forests in its habitat almost always consist of hickory trees, as they are the primary food plant of its caterpillars. Adult butterflies feed on the nectar of a variety of flowering plants including common milkweed, New Jersey tea, and white sweet clover. The hickory hairstreak is a relatively small butterfly with a wingspan of approximately 1 to 1 ½ inches. It is rarely seen with its wings open and is identified by the dark postmedian “dashes” and white outline on the underside of its grayish brown wings. On the hindwing, there is a pale blue patch that extends inward further than the adjacent orange and black spots. There is one tail on each hindwing.
