The Complicated History of Our Marshes and an Update on Restoration Progress
by Caroline Abramowitz, CWF Biological Technician
When looking at the expansive mudflats along the marshes of the Delaware Bay, it is hard to imagine that the area was once densely vegetated and home to a variety of bird species. This spring, CWF began work on a new marsh restoration project funded by the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation and led by Ducks Unlimited and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). CWF was contracted to assist with biological monitoring at sites targeted for marsh restoration along New Jersey’s side of the Delaware Bay. Restoration efforts for our sites are being directed toward mudflats that exist due to significant physical alterations made to the marsh in the past. The story of how these mudflats came to be lies in the area’s history and roots in salt hay farming.
As early as 1675, settlers arriving on the Delaware Bay built dikes in salt marshes to protect land from saltwater inflow and create an environment more conducive to salt hay farming and development. One of the most important types of salt hay harvested along the Delaware Bay was Spartina patens, a crop that was widely used as bedding and feed for livestock due to its high nutritional value. By the mid-1800s, at least 14,000 acres of marsh were impounded in Salem County alone with comparable areas altered in both Cumberland and Cape May counties (Cook, 1870). Impoundments restricted tidal flow within the marsh, which stopped the natural process of marsh accretion in which sediment is consistently added to the marsh to increase its elevation. Additionally, drier conditions exposed marsh soil to too much air, resulting in the breakdown of soil and further loss of elevation.
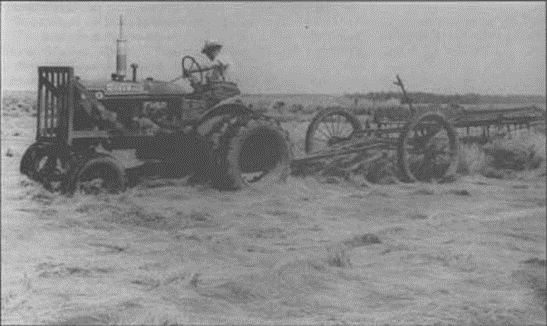
Photo retrieved from”From Marsh to Farm: The Landscape Transformation of Coastal New Jersey,” by Kimberly R. Sebold.
Retrieved through https://www.nps.gov/parkhistory/online_books/nj3/contents.htm