Climate Change is Threatening the Existence of the World’s Most Amazing Bird
By: Lindsay McNamara, Communications Coordinator
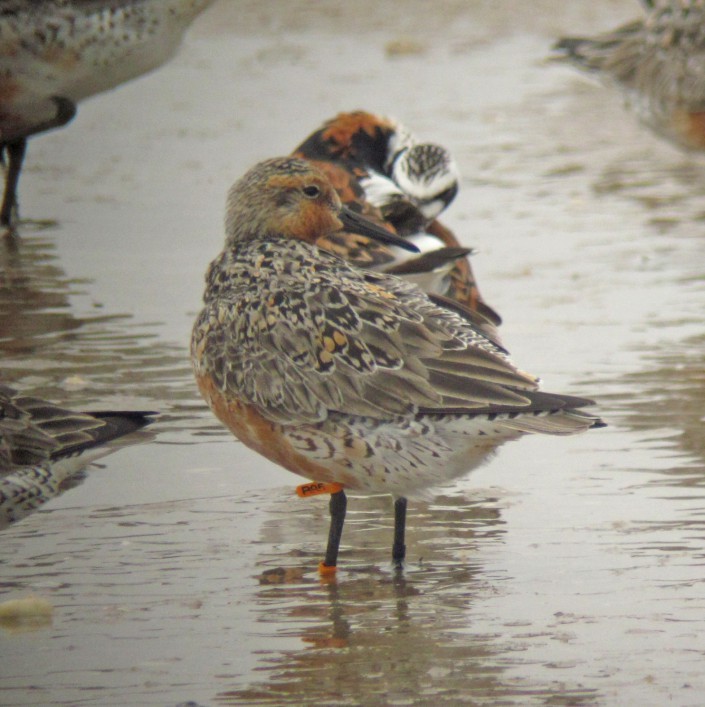

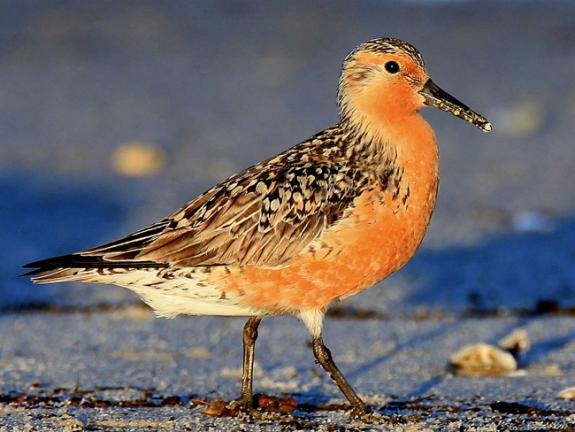
“Moonbird is the most famous, charismatic member of a group of mid-sized shorebirds called Rufa red knots, whose numbers have plummeted so dramatically in the past several decades that they just became the first bird ever listed under the Endangered Species Act with climate change cited as a “primary threat.”
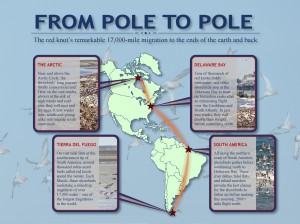
Rufa red knots are among the avian world’s most extreme long range flyers (especially in light of their relatively small size). They travel vast distances — some flying over 18,000 miles — in the course of an annual migration that begins in Tierra del Fuego, Argentina, and extends all the way up to the Canadian Arctic (and back again).
Which brings us to Moonbird’s distinction: Because he is so old — he is at least 21 — he is believed to have flown as many as 400,000 miles in his lifetime. The distance to the moon varies, depending on where it is in its orbit, but the average distance is about 237,000 miles. Thus, Moonbird has not only flown the distance it takes to reach the moon — he has also covered the bulk of the return voyage.
Assuming that Moonbird is still living — the last sighting was in May — there are reasons to wonder whether there will ever be another bird that is his equal. Why? Simply put, his subspecies has been devastated, and climate change will only make matters worse — making extreme survival of the sort that Moonbird has achieved that much more difficult.”
Washington Post Science and Environment Reporter Chris Mooney explores Moonbird’s journey, threats to the species, and the recent Endangered Species Act listing of the Rufa Red Knot:
Learn more:
- On Conserve Wildlife Foundation’s blog: Wildlife Beach Restoration Groups Applaud Endangered Species Act Designation for Red Knot
- Read the Press of Atlantic City article: New Jersey shorebird to get new federal protections
- Conserve Wildlife Foundation’s Delaware Bay Shorebird Conservation Project
- Become a Delaware Bay Shorebird Steward!
Lindsay McNamara is the Communications Coordinator for Conserve Wildlife Foundation of New Jersey.