International Migratory Bird Day Series: American Kestrel
CWF is celebrating International Migratory Bird Day all Week Long
by Lindsay McNamara, Communications Manager
CWF’s blog on the American kestrel is the fifth in a series of five to be posted this week in celebration of International Migratory Bird Day (IMBD). IMBD 2016 is Saturday, May 14. This #birdyear, we are honoring 100 years of the Migratory Bird Treaty. This landmark treat has protected nearly all migratory bird species in the U.S. and Canada for the last century.
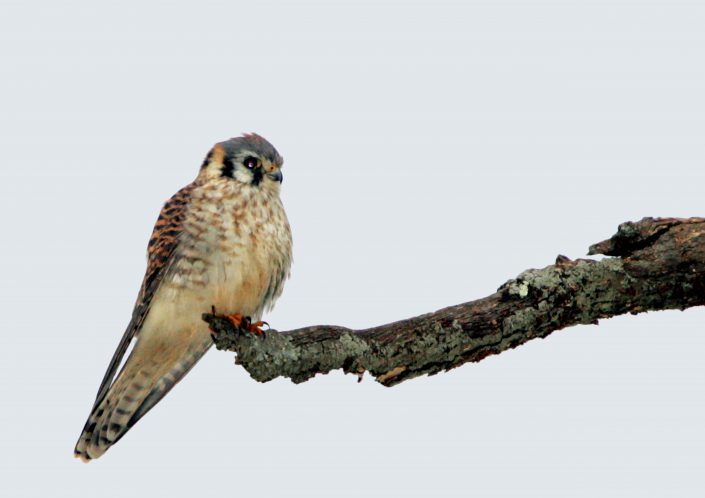

In New Jersey, catching a glimpse of an American kestrel is a rare treat! These beautiful, colorful birds of prey are about the size of a mourning dove — they are the smallest falcon in North America. Kestrels are one of two falcon species that nest in New Jersey.
American kestrels are opportunistic hunters, feeding on a number of different animals like grasshoppers, lizards, mice, snakes and small birds. Unlike peregrine falcons, kestrels don’t use speed to kill their prey. They perch to see their target and then use a stationary, hovering flight that allows them to dive down short distances to capture their prey. The eyespots of a kestrel make it appear to be “looking” up at its aerial predators, like Cooper’s hawks, causing the predators to move on to find a less “alert-looking” target. The eyespots give kestrels the opportunity to focus on hunting for prey beneath them.
Kestrels also hide surplus prey in grass clumps, tree roots, bushes, fence posts, tree limbs, and cavities, to save the food for lean times or to hide it from potential thieves!
Kestrels utilize these hunting tactics in open, grassy habitats — especially ones with cavities for nesting and perches for hunting. Kestrels can be seen hovering in grasslands, pastures and parklands or perched along the road on telephone lines.
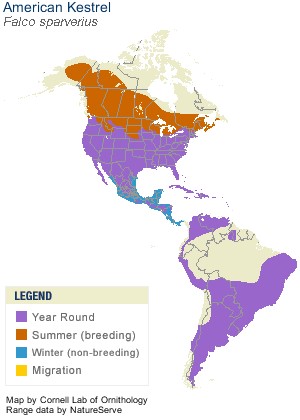 Kestrels can be found in both North and South America, from Alaska and Canada in the north to Argentina in the south. During winter in North America, they will migrate southward from the northernmost portion of their range. They live year-round within New Jersey.
Kestrels can be found in both North and South America, from Alaska and Canada in the north to Argentina in the south. During winter in North America, they will migrate southward from the northernmost portion of their range. They live year-round within New Jersey.
Although the American kestrel is widespread, meaning they live year round throughout much of the United States, the northeastern kestrel population is declining. Today, the kestrel is listed as a threatened species in New Jersey.
The decline of kestrels in New Jersey is likely due to destruction of grasslands from development. Nesting cavities are also being lost. As humans clean up fields, we remove trees with nest cavities that kestrels use. Kestrels are secondary cavity nesters. They don’t make their own cavity but use existing natural or man-made cavities.
Since kestrels nest in buildings and other man-made structures, nest box programs are an effective way to help grow the number of kestrels in areas where nest sites are limited.
Conserve Wildlife Foundation of New Jersey, in partnership with the Endangered and Nongame Species Program implemented a nest box installation and monitoring program in 2006. Nest boxes have been placed in areas of habitat determined to be suitable for the birds of prey. The boxes are monitored by biologists during the breeding season. Because kestrels reuse nest sites, particularly if they have successfully raised young, we focus on boxes that have been successful at least once since 2006.
The nest box program in New Jersey appears to be successful; we are adding to the population. Since 2006, we have banded over 300 fledglings. You can help too! Next time you see an American kestrel in the Garden State, be sure to submit a Rare Species Sighting form.
Learn More:
Lindsay McNamara is the Communications Manager for Conserve Wildlife Foundation of New Jersey.
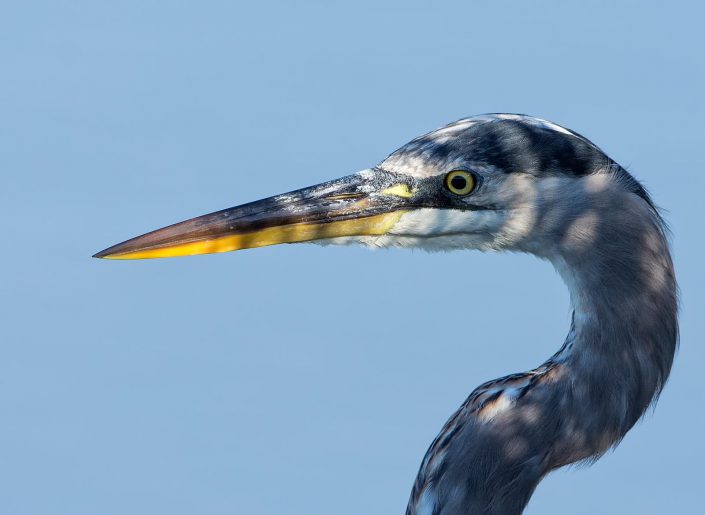


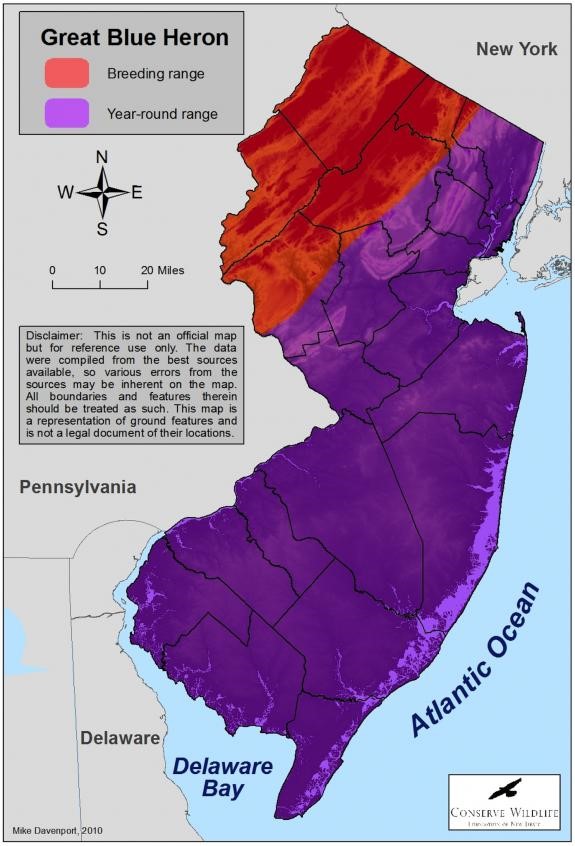 The great blue heron occurs throughout most of North America, from Alaska and eastern Canada in the north to the northern portion of South America in the south. Northern populations of great blue herons east of the Rockies are migratory.
The great blue heron occurs throughout most of North America, from Alaska and eastern Canada in the north to the northern portion of South America in the south. Northern populations of great blue herons east of the Rockies are migratory.